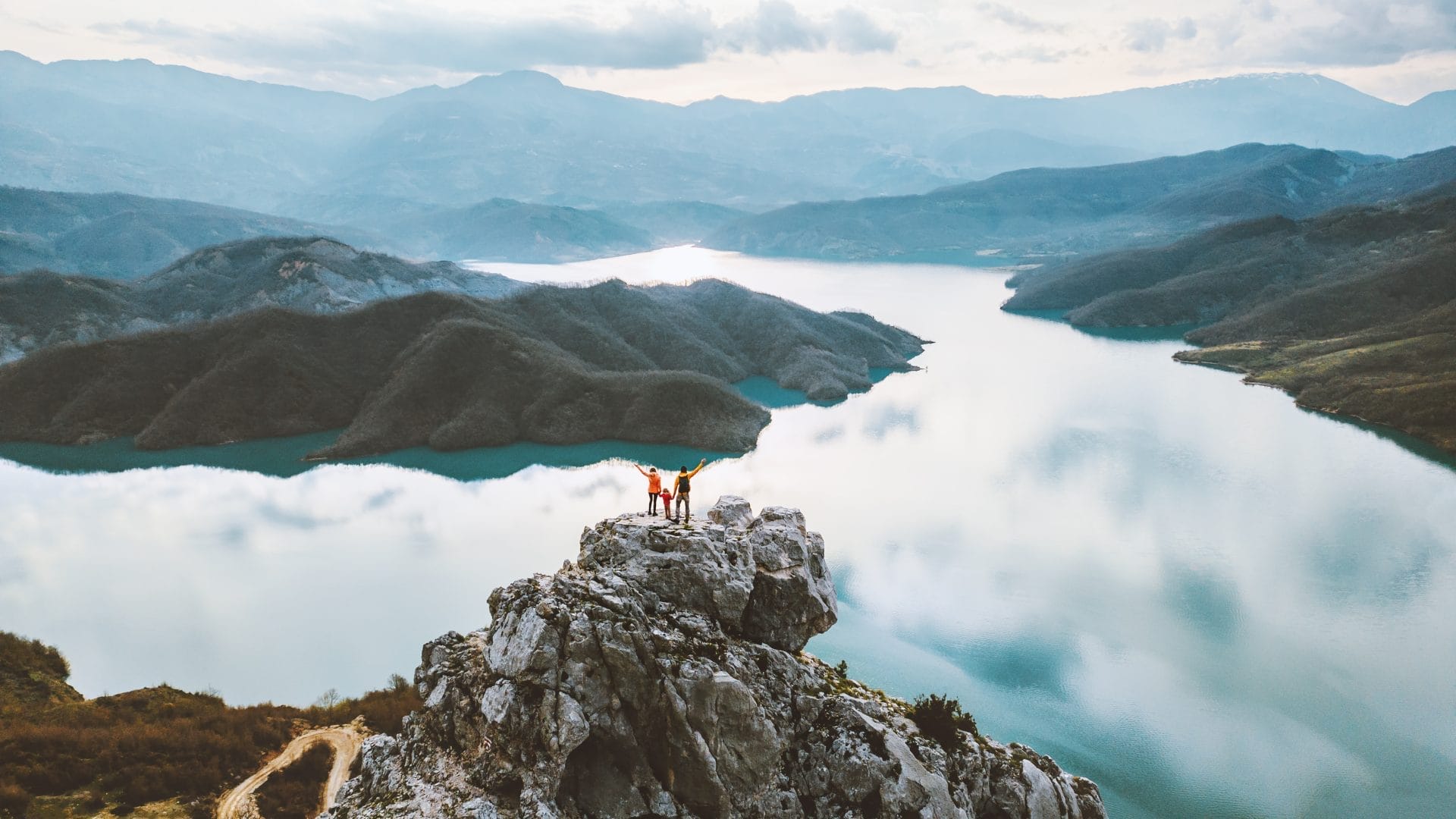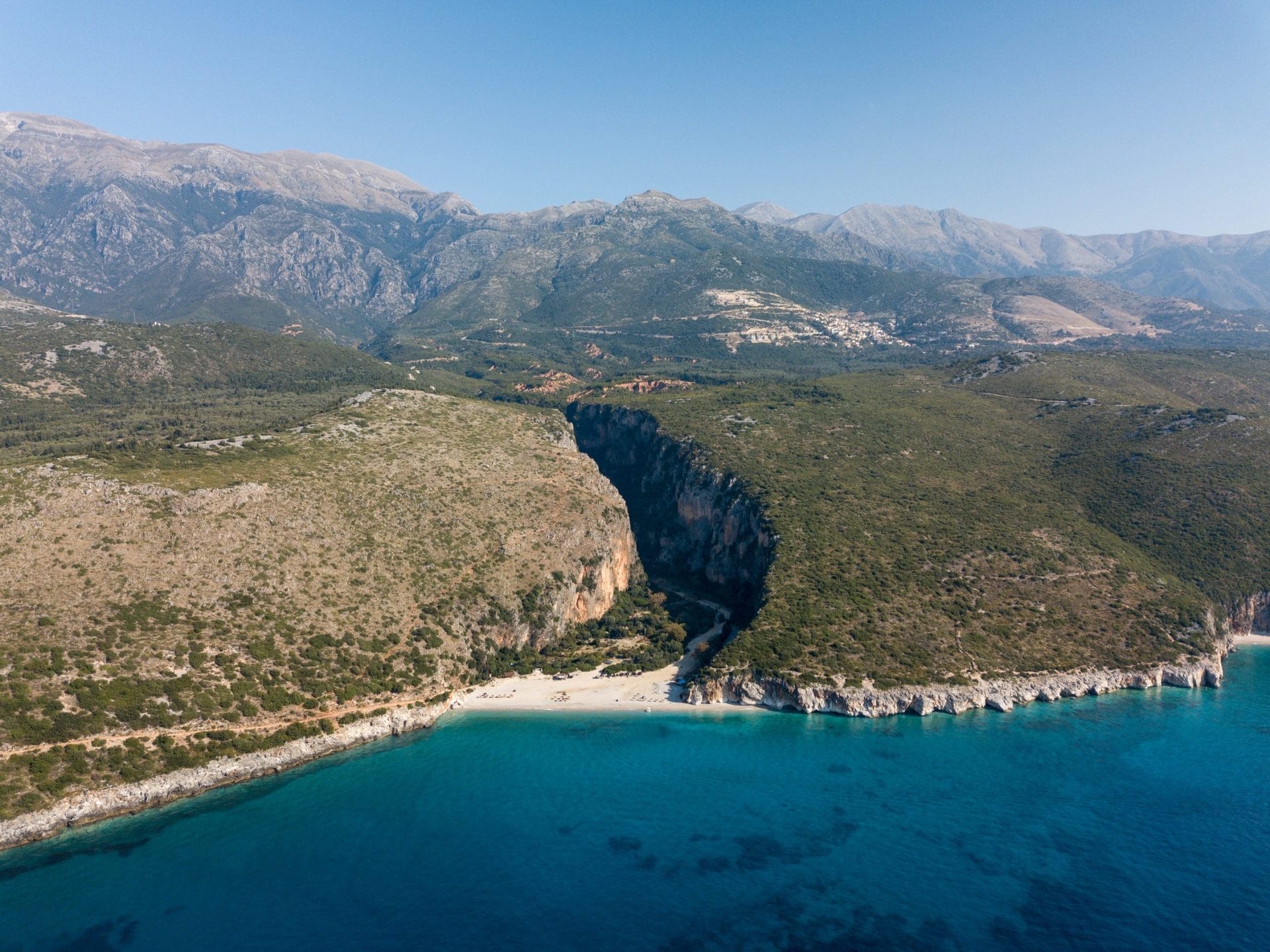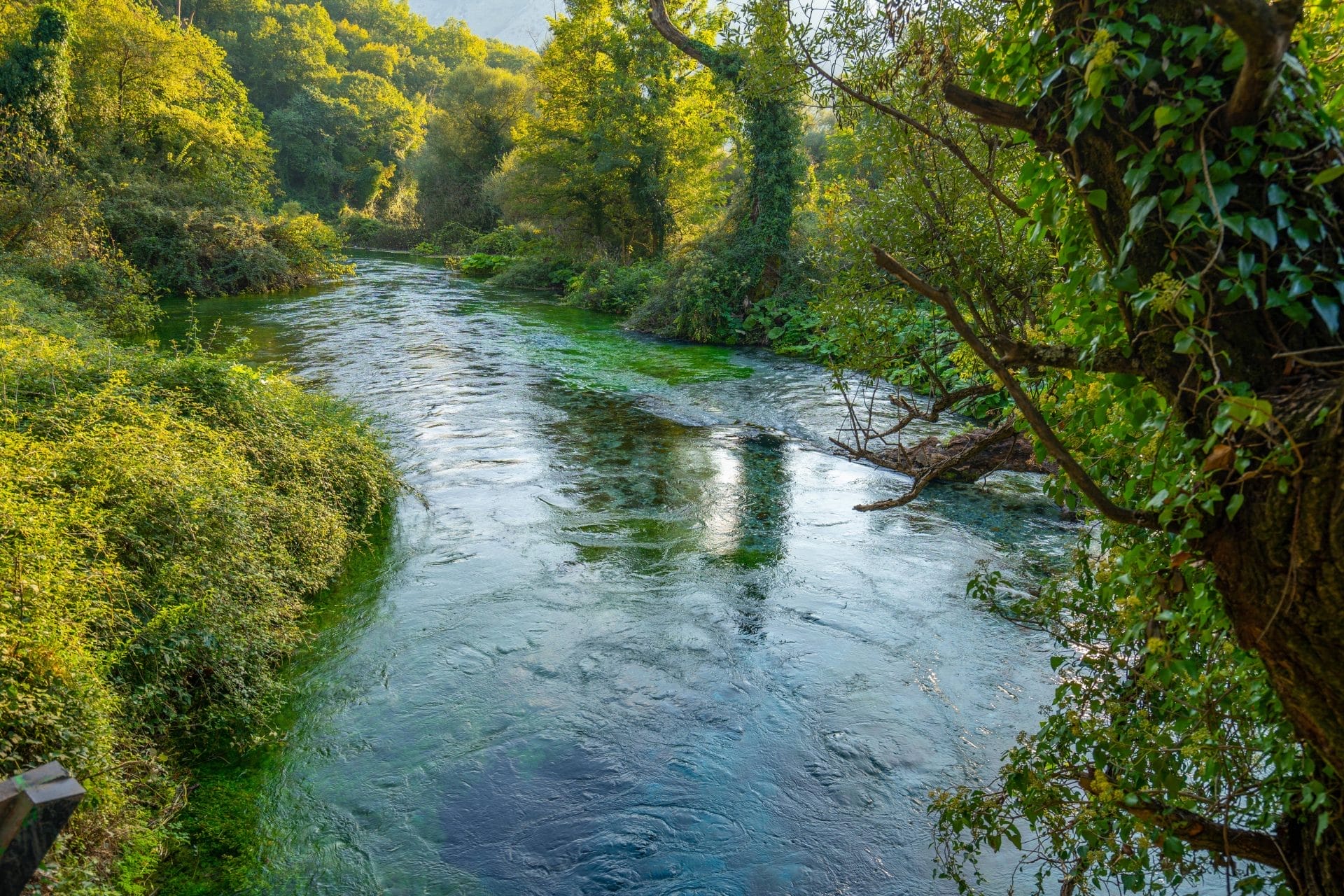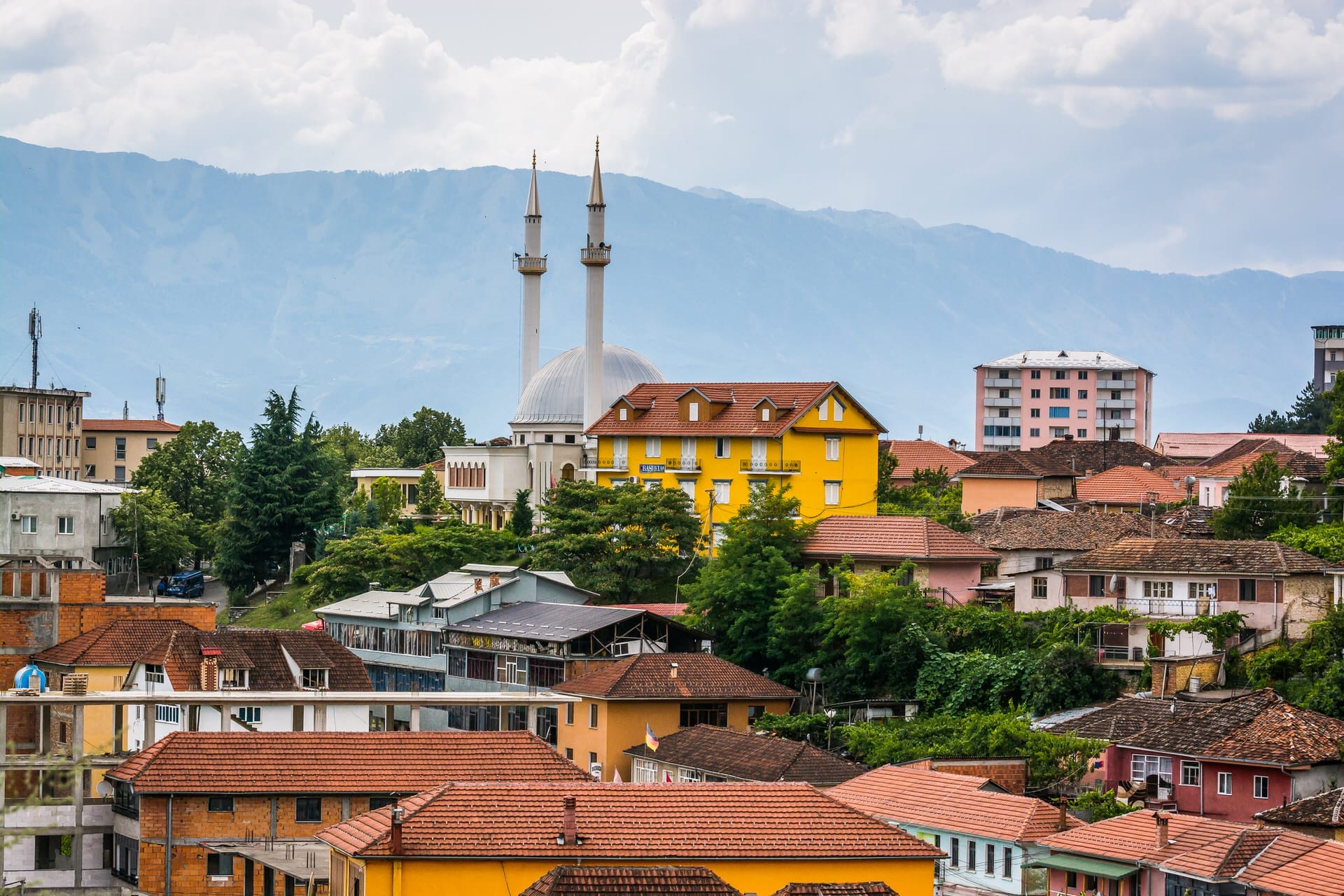
The Dawn of Civilization
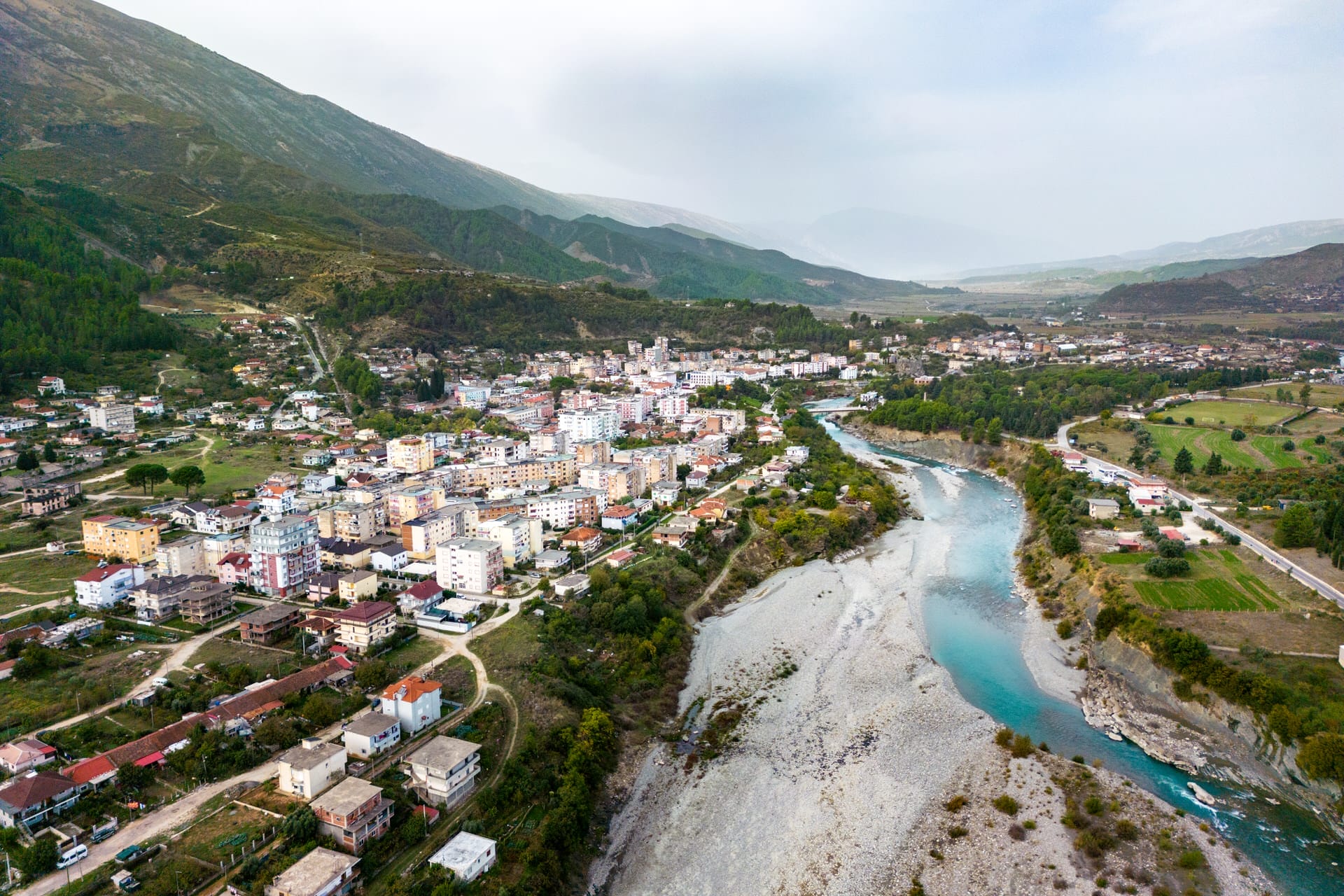
The earliest inhabitants of Albania were hardy, nomadic people, existing in a world that seemed almost impossible to survive in. Yet, they thrived, adapting to the harsh conditions and mastering the art of survival. Evidence of their existence can be found in the Middle and Upper Paleolithic eras through excavations of important sites like Xarrë and Dajti.
Archaeologists, with their keen eyes and delicate tools, have unearthed valuable artifacts from these sites, offering a glimpse into the daily lives of these early Albanians. Stone tools used for hunting and gathering have been discovered alongside fragments of animal bones, indicating that these people were skilled hunters and resourceful gatherers.
But perhaps even more intriguing are the connections that these findings reveal between Albania and its neighboring regions. Through trade and migration, it is clear that the early Albanians had close ties with the people of Montenegro and Greece. These connections paint a picture of a bustling, interconnected world long before the modern borders were drawn.
The Arrival And Lives Of The Illyrians
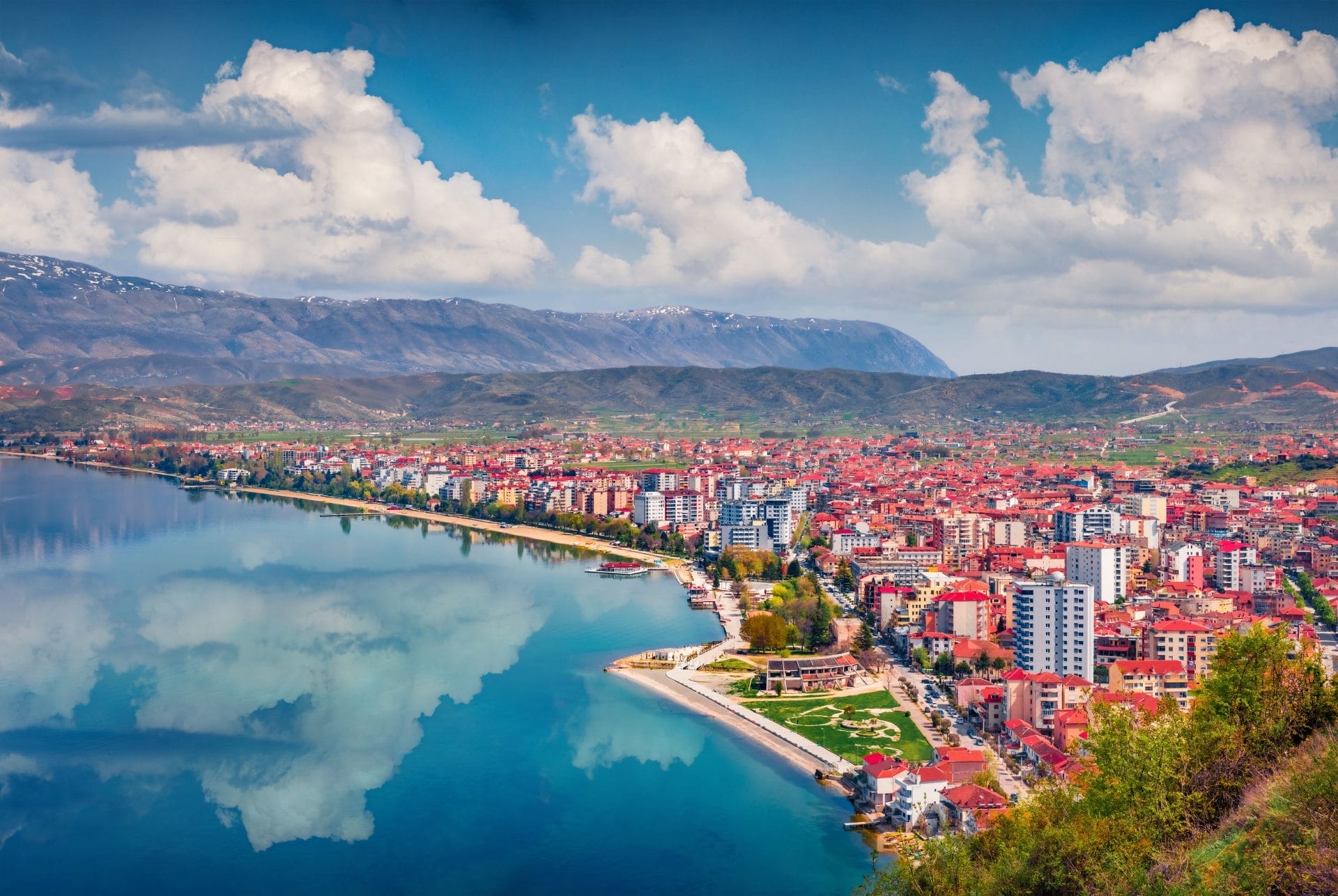
Around 2000 BCE, the Illyrian tribes had established their presence in the hills and fields of the Balkan region. These pastoralists, who belonged to the Indo-European group, strategically settled in elevated areas that were easier to defend. As they entered the Bronze Age, their way of life revolved around herding animals, farming, fishing, and basic metalworking. Excavations by archaeologists have revealed remnants of their homes and burial grounds, providing insight into the mysterious Illyrian culture.
The Bronze And Iron Ages
The arrival of the Bronze Age brought about significant progress for the early inhabitants of Albania, as they were able to increase contact and trade with neighboring societies. The possession of superior bronze weapons, tools, and ornaments became a way for tribal leaders to display their status. By 1000 BCE, the shift to the Iron Age enabled the Illyrians to improve their agriculture, mining, and military tactics, solidifying their dominance in the area.
Complex Society, Arts And Culture
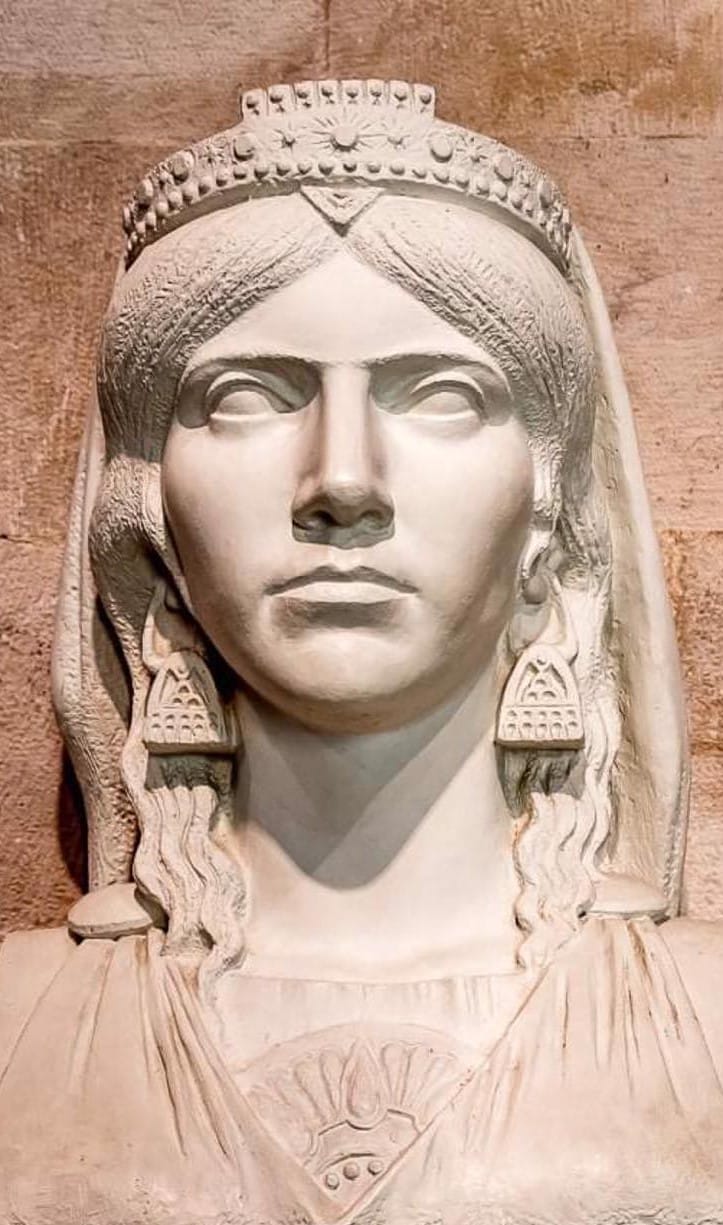
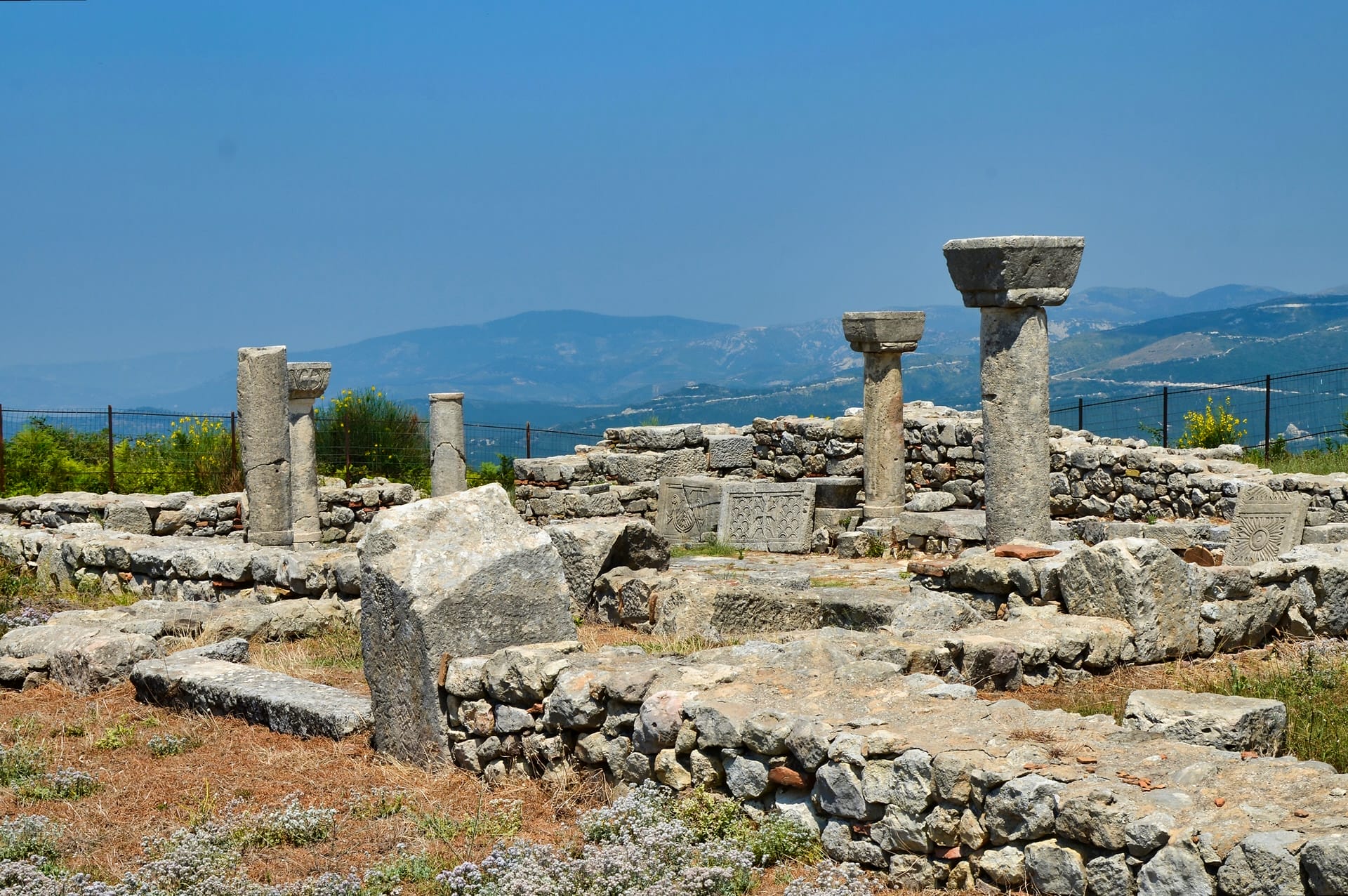
The social structures of Illyria became increasingly intricate, with a select group of warriors and priests holding the most power. Evidence of this can be seen in burial sites, which often included elaborate displays of wealth and adoration for ruling families. The people of Illyria were also highly skilled in metalworking, as seen in their delicate craftsmanship on items such as pottery, figurines, and jewelry.
Greek Colonization And Influence
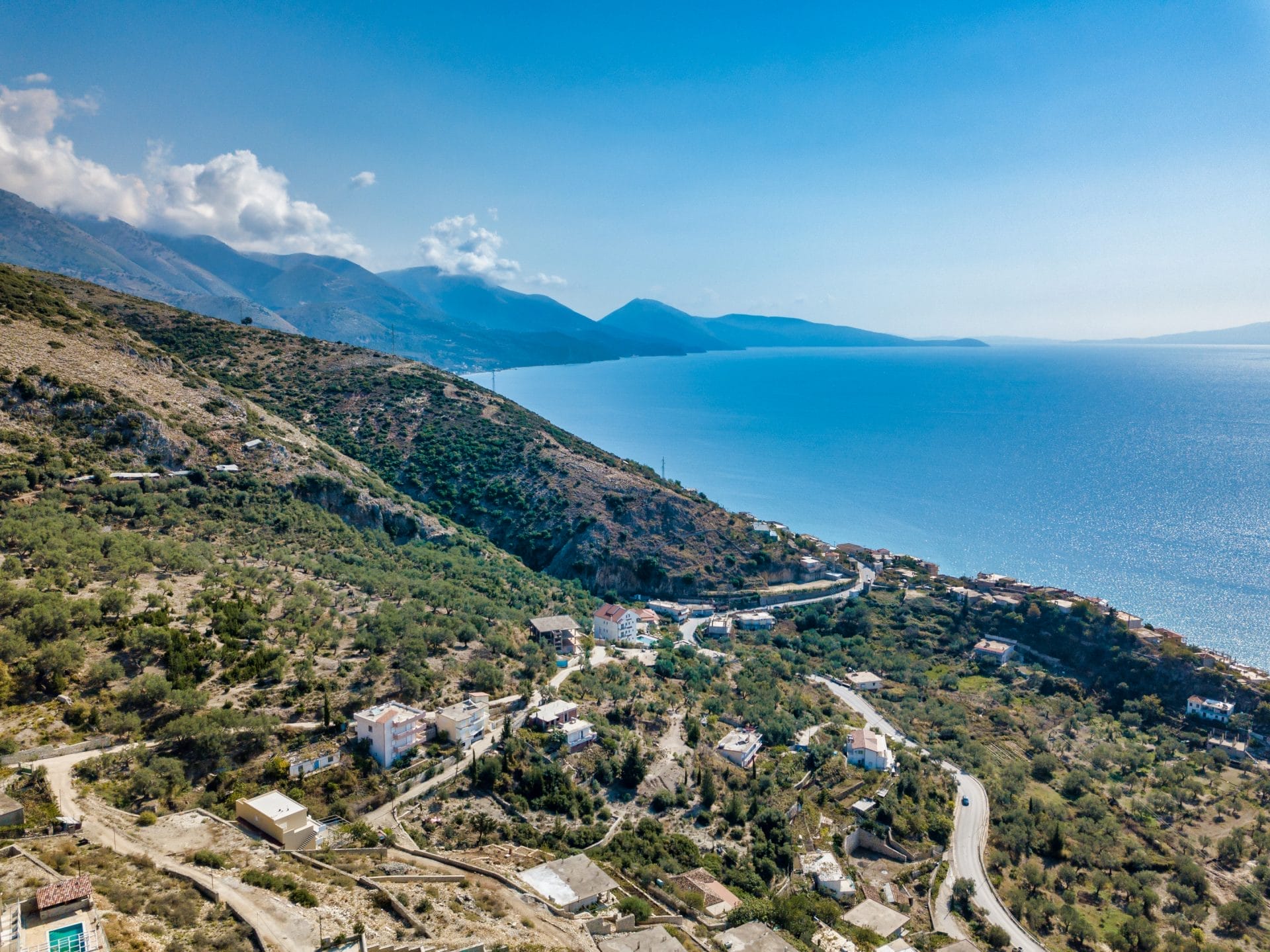
Around the 7th century BCE, Greek merchants from cities such as Corinth began sailing along the Adriatic coast, establishing trading outposts known as emporia. These settlements were located strategically, allowing easy access to local resources and markets. This influx of Greek merchants introduced new goods and ideas to the Illyrian tribes, including pottery, wine, olive oil, and bronze objects.
The Greek colonies along the Illyrian coast quickly became hubs for trade and cultural exchange between the Greeks and the Illyrians, increasing demand for Illyrian products such as timber, copper, iron, and livestock. In return, the Illyrians gained access to Mediterranean goods and technologies that greatly influenced their way of life.
As a result of this interaction, aspects of Hellenic culture began to spread among the Illyrians. This included architectural styles, language (with some Greek loanwords incorporated into Illyrian), religious beliefs (such as the worship of Greek gods like Zeus and Apollo), and artistic techniques (such as pottery making).
Illyrian Resistance And Assimilation
While some inland tribes readily adopted Hellenic customs and practices through trade and political alliances with neighboring Greek cities, others resisted this influence. They saw it as a threat to their traditional way of life and formed partnerships with other tribes or used guerrilla tactics against Greek settlements. However, over time, many Illyrian tribes gradually assimilated certain aspects of Hellenic culture through continued contact with Greek colonies.
The effects of Greek colonization in ancient Albania were extensive and enduring. It not only resulted in economic advantages but also had a major influence on the cultural and societal progress of the region.
Roman Conquest
In the 2nd century BCE, the Roman Republic expanded its territory into Illyria. The Illyrians, known for their fierce resistance and skilled warriors, fought tough against the Romans. However, they could not withstand Rome’s legions’ advanced military tactics and superior weaponry. By 168 BCE, most of modern-day Albania had fallen under Roman control. This began a new era for the region and its people.
Under Roman rule, the territories of Illyria were gradually assimilated into the Roman Empire. This process, known as Romanization, involved adopting elements of Roman culture such as language, customs, architecture, and religion.
As new cities were established and existing ones expanded, many Illyrian settlements were Hellenized with a distinct blend of Greek and Roman influences. Latin became the official language in these cities and was used for trade and administration.
The influx of Roman influence also brought about significant changes in society and economy. Establishing new cities led to increased urbanization, creating new social classes and opportunities for trade and commerce. The introduction of Roman laws and institutions also brought about a more organized system of government in which local elites could rise to positions of power within the empire.
Remnants Of Illyrian Culture
Despite being conquered by Rome, many aspects of Illyrian culture persisted among local tribes in rural areas. These included traditional customs such as blood feuds (known as “kanun” in Albanian), cultural practices related to agriculture and animal husbandry, and religious beliefs tied to nature worship. The legacy of Illyrian culture can also be seen in modern-day Albania through place names that have roots in ancient Illyrian words.